Did You Know Multi-Cloud And Multiple Cloud Mean Different Things?
 By Anita Srinivasan
By Anita Srinivasan
 20th October, 2023
20th October, 2023
Multi-Cloud Integration
Multi-Cloud Best Practices
Multi-Cloud Strategy
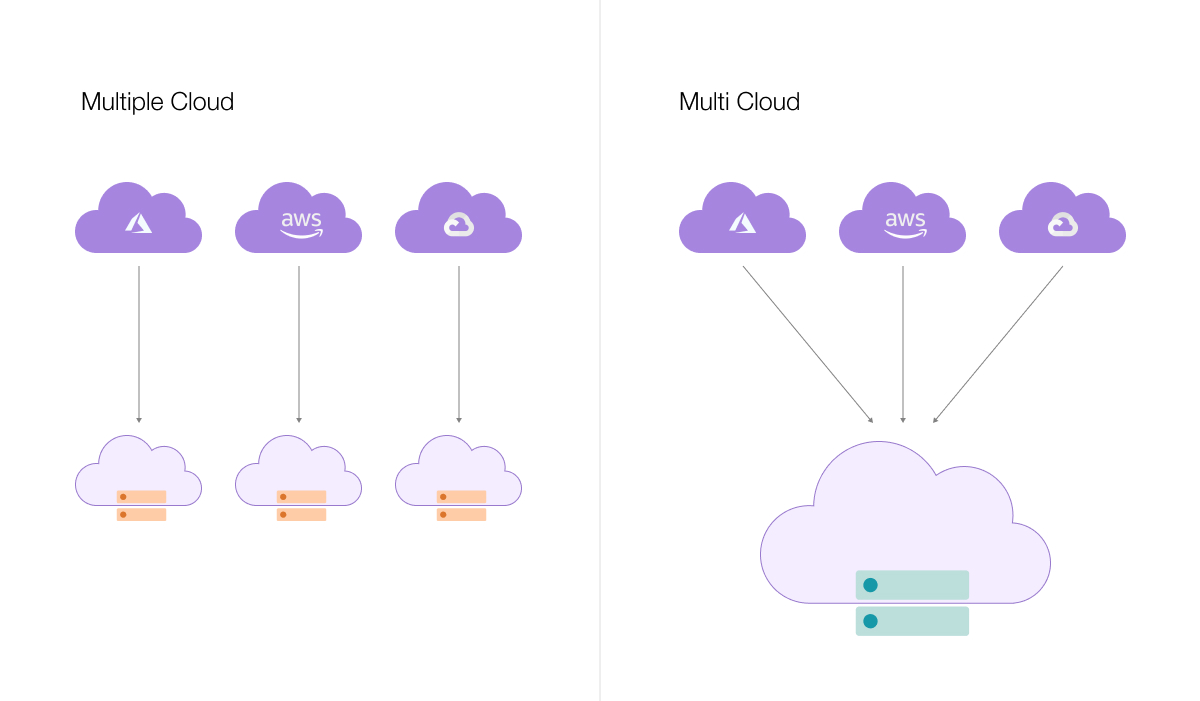
In the rapidly evolving world of Cloud Computing, two terms that often appear similar but are largely different from one another, are Multi-Cloud, and multiple-cloud.
Today, we want to help you understand these terms better, what do they mean individually? What benefits do they bring to the table and, how are they different?
For an in-depth understanding of Cloud Migration strategies, best practices, and approaches, download our exclusive whitepaper resource.
As more organizations are moving to the cloud and leveraging cloud computing solutions for their IT infrastructure, understanding these differences becomes crucial.
Often confused with one another, Multi-Cloud and Multiple Cloud represent distinct approaches to cloud deployment and management.
In this blog post, we will delve into the nuances of these terms and explore how each approach impacts your organization.
THE MULTI CLOUD- A STRATEGIC APPROACH
Multi-cloud is a cloud computing strategy that uses services and resources from multiple cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) simultaneously.
Instead of relying on a single cloud provider, organizations using a multi-cloud approach distribute their workloads and applications across different cloud platforms based on the specific needs and strengths of every Cloud Computing Service provider.
The key idea is to avoid vendor lock-in and leverage the strengths of various cloud platforms for specific tasks or workloads.
HOW IS MULTI-CLOUD USEFUL?
- Reduced Vendor Lock-In
Multi-cloud strategies try to avoid dependency on a single cloud provider. By using several cloud platforms, organizations can prevent being restricted to one vendor’s technologies and pricing structures. - Optimized Performance
Different cloud providers have their own set of strengths and capabilities. By strategically assigning workloads to the most suitable cloud platform organizations can improve performance and enhance cost efficiency. For example, they may use AWS for compute-intensive tasks and GCP for machine learning. - Enhanced Reliability
Multi-cloud can provide redundancy and failover options. If one cloud provider experiences downtime or issues, the organization can easily shift its operations to another provider. - Compliance and Data Sovereignty
Organizations can choose specific cloud providers based on compliance and data sovereignty requirements. For instance, a company subject to strict data regulations in different regions may opt for cloud providers with data centres in those regions. - Cost Optimization
Multi-cloud strategies can be used to take advantage of cost variations between cloud providers. It involves cost-conscious decision-making, where workloads are allocated to the provider offering the most cost-effective solutions. - Disaster Recovery
Multi-cloud can help with disaster recovery and business continuity. Data and applications can be duplicated across multiple cloud providers to ensure high availability and data resilience. - Flexibility and Innovation
By having access to various cloud ecosystems, organizations can leverage the latest innovations and technologies offered by different providers. This enables them to stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
Implementing a multi-cloud strategy requires careful planning, management, and monitoring to ensure the various cloud environments work seamlessly together.
To understand if Cloud Computing is worth your investment, check out our informational video by clicking on this link.
UNDERSTANDING THE MULTIPLE CLOUD APPROACH
“Multiple cloud” is a less common term, but it could be used in a general sense to describe an environment where an organization uses multiple instances or deployments of a single cloud provider’s services.
THE “MULTIPLE CLOUD” SCENARIO CAN RESULT IN
- Lack of Coordination
Users or departments within an organization may independently adopt cloud services without a clear strategic plan for integration or coordination. It can result in a scattered approach where various cloud services are used without considering how they interact or share data. - Data Silos
Since different cloud services or platforms are not integrated or coordinated, data may become fragmented and isolated within these services, making it challenging to share or analyze data across the various cloud environments. - Resource Inefficiency
Using multiple cloud services without a strategic plan can lead to resource inefficiency, as users may not take advantage of cost-saving opportunities or optimized configurations. - Increased Complexity
Managing and securing several disconnected cloud services can be more complex and challenging compared to a well-coordinated multi-cloud approach. - Security and Compliance Risks
When various cloud services are utilized without a comprehensive strategy, it can introduce security and compliance risks, as each service may have different security and compliance requirements.
Let us now help you clearly understand the distinguishing factors between Multi-Cloud and Multiple- Cloud:
MULTI-CLOUD VS. MULTIPLE CLOUD
- Multi-Cloud maintains a single copy of the data that can be accessible from all cloud environments simultaneously. Multiple Cloud gives way to duplicate data, where each copy of the data can be accessed from a single cloud.
- Multi-Cloud avoids vendor lock-in. Multiple Clouds presents users with complex integration and data management methods.
- In Multi-Cloud, organizations can select the right cloud computing services and resources. In Multiple Clouds, organizations must work with multiple IPs and volumes of data.
- In Multi-Cloud, organizations can receive accurate cost savings that in turn help them gain cost predictions. In Multiple Clouds, egress charges are unpredictable, and organizations are also burdened with data transfer expenses.
- In Multi-Cloud, organizations can experience a data-driven digital transformation of their IT infrastructure. Multiple Cloud opens up organizations to issues about synchronization.
Remember, the distinction between multi-cloud and multiple cloud is rather a strategic choice that can significantly impact an organization’s cloud computing experience.
Multi-cloud is a strategic approach, where careful planning, integration, and vendor diversification lead to optimized performance, cost efficiency, and risk reduction.
On the other hand, multiple cloud often uses a decentralized adoption that may create complexities, inefficiencies, and data silos. Businesses must recognize the significant differences between these two approaches and carefully decide which one aligns best with their goals, resources, and long-term cloud strategy.
Ultimately, the choice between multi-cloud and multiple cloud depends on how an organization wants to harness the limitless potential of the Cloud.
If you would like to understand our Cloud Computing and Cloud Migration approaches, please visit our website for insightful case studies and whitepapers.
References:
Is my data architecture multi-cloud or multiple cloud? (CloudTweaks)